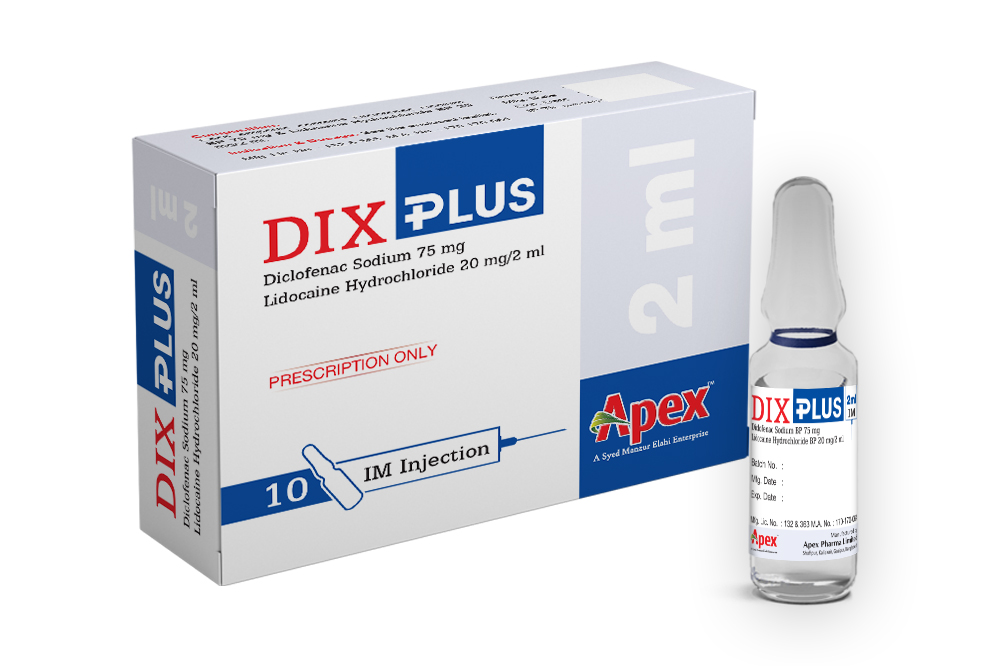
Dix Plus
Home / By Brand Name / Dix Plus
Description:
Diclofenac is a potent non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with marked analgesic and antipyretic properties. It also has some uricosuric effect. The actions of diclofenac appear to be associated principally with the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. Diclofenac may inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cycloxygenase, an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of prostalandin precursors (endoperoxides) from arachidonic acid. Lidocaine is the most widely used local anaesthetic drug. It acts more rapidly and is more stable than most other local anaesthetics. It is a very useful surface anaesthetic. Like other local anaesthetic, lidocaine imparis the generation and conduction of the nerve impulses by slowing depolarization. Peak plasma concentration of diclofenac is achieved within half-an hour following injection. Lidocaine is effectively absorbed from mucous membranes. Diclofenac is 99.7% plasma protein bound and plasma half-life for the terminal elimination phase is 1- 2 hours. It also enters the synovial fluid, where maximum concentrations are measured 2-4 hours after the peak plasma values have been obtained. The apparent half-life for elimination from the synovial fluid in 3-6 hours. The onset of anaesthesia of Lidocaine HCl is more rapid and the duration of action is longer. A 1%-2% solution has a duration of action of about 1-2 hours. Binding of lidocaine to plasma proteins is variable and concentraion dependent. Diclofenac is extensively metabolized to a range of phenolic compounds. About 60% of the administered dose is excreted via the kidneys in the form of metabolites and less than 1% in unchanged form. The remain is excreted via the bile in metabolized form. Approximately 90% of a parenteral dose of lidocaine is rapidly metabolized in the liver. Less that 10% of a dose is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Composition :
Each 2 ml ampoule contains Diclofenac sodium BP 75 mg and Lidocaine Hydrochloride USP 20 mg.
Indications :
Dix plus Injection diclofenac sodium, which has got the following
therapeutic uses :
1) Rheumatoid Arthritis, 2) Osteoarthritis, 3) Low back pain and other acute musculokeletal disorders such as periarthritis (e.g., frozen shoulder), tendinitis, tenosynovitis, bursitis, sprains, strains and dislocations, 4) Ankylosig spondylitis, 5) Acute gout, 6) Acute trauma and fractures, 7) Control of pain and inflammation in orthopaedic, dental and other minor surgery, 8) Juvenile chronic arthritis, 9) Postoperative pain, 10) Pain of renal colic, & 11)
Other uses.
Dix plus Injection also contains lidocaine, which acts as a local anaesthetic. Therefore, the possibility of pain at the injection site, which is most likely to occur after intramuscular injection of normal diclofenac, is minimized if Dix plus Injection is used in the above indications.
Dosage and Administration :
Adults: One ampoule once (or in severe cases, twice) daily by intramuscular injection.
Renal colic: One ampoule once daily intramuscularly. A further ampoule may be administered after 30 minutes, if necessary. The recommended maximum daily dose of diclofenac and lidocaine is 150 mg and 200 mg, respectively, by any route.
Children :
In juvenile chronic arthritis, 1-3 mg of diclofenac / kg body wt. daily in divided doses.
Elderly patients :
In elderly or debilitated patients, the lowest effective dosage is recommended, commensurate with age and physical status. or as prescribed by the physician.
Precautions :
History of gastro-intestinal ulceration, haematemesis or melaena, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, bleeding diathesis or haematological abnormalitits. Patients with severe hepatic, cardiac or renal insufficiency or the elderly should be kept under close surveillance. All patients who are receiving long term treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents should be monitored as a precautionary measure (e.g., renal, hepatic function and blood counts.)
Use in pregnancy & lactation :
It should not be prescribed during pregnancy, unless there are compelling reasons for doing so. The lowest effective dosage should be used. This type of drug is not recommended during the last trimester of pregnancy. Very small quantities of diclofenac may be detected in breast milk, but no undesirable effects on the infant are to be expected.
Contraindications :
It is contraindicated for those patients who are hypersensitive to diclofenac. In patients with active or suspected peptic ulcer or gastrointestinal bleeding, or for those patients in whom attacks of asthma, urticaria or acute rhinitis are precipitated by aspirin or other NSAID's possessing prostaglandin synthetase inhibiting activity, it is also contraindicated. Because of the presence of lidocaine, it is also contraindicated for those patients who are hypersensitive to local anaesthetics of the amide type, although the incidence is very rare. In patients with Adams-Stokes
syndrome or with severe degrees of SA, AV or intraventricular heart block in the absence of an artificial pacemake, and for those patients who are hypersensitive to any of the excipients used in the formulation (sodium metabisulphue, mannitol, benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol), this injection is also contra-indicated.
Side-effects :
Side-effect to diclofenac and lidocaine injection are usefully mild and transient, However, if serious side-effects occur, the injection
should be discontinued. Gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, diarrhoea and occasionally bleeding may occur. In very rare instances, injection site disorders may occur. In isolated cases, abscesses and local necrosis may occur. The adverse effects due to lidocaine mainly involve the CNS, are usually of short duration, and are dose related. The CNS reaction may be manifested by drowsiness, dizziness, disorientation, confusion,
lightheadedness etc.
Store in a place which protects from heat and light.
PRODUCTS