Flunarin
Home / By Brand Name / Flunarin
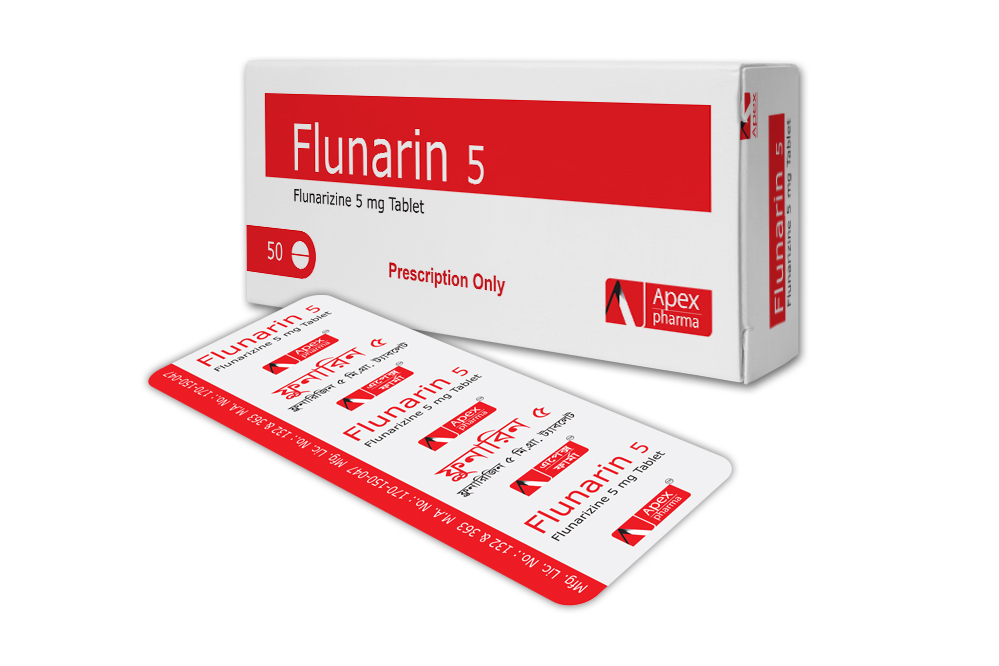
Flunarin
Generic Name: Flunarizine
Therapeutic Class: Antimigraine & Antivertigo
Composition
Flunarin-5 Tablet: Each film coated tablet contains Flunarizine Hydrochloride BP equivalent to 5 mg Flunarizine.
Flunarin-10 Tablet: Each film coated tablet contains Flunarizine Hydrochloride BP equivalent to 10 mg Flunarizine.
Description
Flunarin is the preperation of Flunarizine Dihydrochloride. Flunarizine is the difluorinated derivative of cinnarizine. Flunarizine is a selective calcium channel antagonist. It prevents cellular calcium overload by reducing excessive transmembrane influxes of calcium. It does not interfere with normal cellular calcium homeostasis. It also has antihistaminic and sedative properties.
Indication
Prophylaxis of classic (with aura) or common (without aura) migraine. Symptomatic treatment of vestibular vertigo, dizziness.
Peripheral vascular disease (Intermittent claudication, Raynaud's phenomenon, paresthesiae, cold extremities, nocturnal cramp and trophic disorders owing to ischaemia of limbs). Refractory epilepsy resistant to conventional antiepileptic therapy.
Alternating hemiplegia of childhood.
Dosage & Administration
The usual dose is 5 to 10 mg daily, usually given at night to minimize the effects of drowsiness.
For migraine prophylaxis: Starting dose is 10 mg daily (at night) for patients less than 65 years and 5 mg daily for patients older than 65 years.
For vertigo: The recommended maximum daily dose of flunarizine in the treatment of vertigo is 10 mg daily in adults and 5 mg daily in children ( < 40 kg).
For epilepsy: An optimal therapeutic dosage in epileptic patients receiving other anti- epileptic drugs is 15 mg to 20 mg daily in adults and 5 to 10 mg daily in children.
Maintenance treatment: If a patient's response is satisfactory and if a maintenance treatment is needed, the dose should be decreased so that each week the patient has 5 days treatment at the same daily dose and 2 successive drug free days. Treatment should be interrupted after 6 months and re-initiated only if the patient relapses. The recommended maximum daily dose is 10 mg daily in adults and 5 mg daily in children (< 40 kg).
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to flunarizine or structurally similar calcium channel blocker Patients with a history of depressive illness Patients with pre-existing symptoms of Parkinson's disease or other extra pyramidal disorders Hepatic insufficiency (relatively contraindicated)
Precaution
Since sedation or drowsiness occur in some patients during treatment with flunarizine hydrochloride, patients should be cautioned against activities which require alertness or rapid, precise responses (e.g. operating machinery or a motor vehicle) until the response to the drug has been determined.
Side Effect
Flunarizine is well tolerated and seldom causes serious side effects. The main adverse effects experienced by the patients are as follows:
Central Nervous System: Depression, drowsiness, sedation, anxiety.
Gastrointestinal: Heart burn, nausea, emesis, dry mouth, gastralgia.
Miscellaneous: Weight gain, and/or increased appetite, asthenia, muscle aches, skin rash, and galactorrhea in female patients on oral contraceptives.
Use In Pregnancy & Lactation
In pregnancy: There is no data to support the use of flunarizine during pregnancy. Therefore it should not be administered to pregnant women unless the anticipated benefits outweigh the potential risks. In lactation: Animal studies have shown that flunarizine is excreted in breast milk. Therefore, breast-feeding should be discouraged in women taking flunarizine.
Drug Interactions
Galactorrhea has been reported in few women on oral contraceptives within the first two months of flunarizine treatment. Hepatic enzyme inducers such as carbamazepine and phenytoin increase the metabolism of flunarizine and thus reduce its steady state level. So an increase in dose of the drug may be required. Concomitant use of a calcium channel blocker and amiodorone has been reported to result in sinus arrest and atrioventricular block. Excessive sedation can occur when alcohol, hypnotics or tranquilizers are taken simultaneously with flunarizine.
Overdose
Acute overdosage has been reported and the observed symptoms were sedation, agitation and tachycardia. Treatment of acute over-dosage consists of charcoal administration, induction of emesis or gastric lavage, and supportive measures. No specific antidote is known.
Store in a cool dry place and from light. Keep out of the reach of children.
PRODUCTS